Fibonacci series program in C using recursion
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where the next number is the addition of the last two numbers, the Fibonacci series starts with 0, and 1.
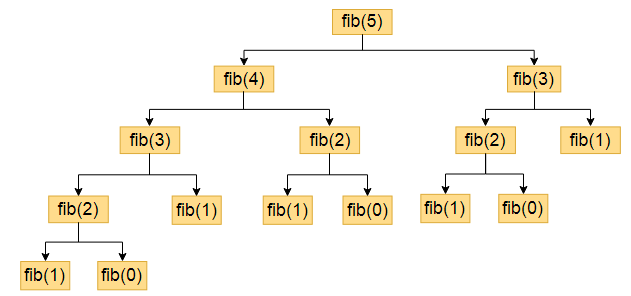
For example, if we want to find Fibonacci of the 5th term then using recursion we will get the following.
fib(5) = fib(4) + fib(3)
fib(4) = fib(3) + fib(2)
fib(3) = fib(2) + fib(1)
fib(2)=fib(1)+fib(0)
fib(1)=1
fib(0)=0
#include<stdio.h>
int fibs(int a)
{
if (a==0)
return 0;
else if(a==1)
return 1;
else
return (fibs(a-1)+fibs(a-2));
}
int main()
{
int a,i,fib;
printf("\n enter the fibonacci length:");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("fibonacci series are:");
for(i=0;i<a;i++)
{
fib=fibs(i);
printf("%d\t",fib);
}
return 0;
}output
enter the fibonacci length:7 fibonacci series are:0 1 1 2 3 5 8
Explanation of Fibonacci series recursive function program
- we declare
fibsfunction i.e Fibonacci series function. it will calculate the Fibonacci series value. - when you run a program, we know our program will always start executing from the
main(). - so first it will take input from a user and stored it in variable
a. - now we call our
fibsfunction from 0 to tillavalue.for(i=0;i<a;i++) { fib=fibs(i); printf("%d\t",fib); } - In a for a loop when
ivalue is 0 it will callfibs(0)function, andfibs(0)function will return a value 0. because inside our fibs function we have writtenif (a==0) return 0; - when
ivalue is 1 it will call fibs(1), the function will return value 1.else if(a==1) return 1; - when
ivalue 2, it will call fibs(2). Infibsfunction, else part gets executed.
Forelse return (fibs(a-1)+fibs(a-2));fibs(2)it call recursively itself for fib(2-1)+ fibs(2-2) i.e fibs(1) and fibs(0). - similarly, it will calculate fibs(3), fibs(4), etc., and print Fibonacci value.